Unveiling The Bold Jumper: North America's Daring Little Predator
The world of spiders often evokes a mix of fascination and apprehension, but few arachnids capture hearts quite like the bold jumper. Known scientifically as *Phidippus audax*, this common species is a true marvel of the insect world, easily identified by its striking appearance and remarkable capabilities. From their large, captivating eyes to their iridescent fangs, bold jumpers are not just spiders; they are tiny, fuzzy acrobats that play a vital role in our ecosystems.
Often referred to as the daring jumping spider, *Phidippus audax* stands out among its kin. Unlike many spiders that rely on intricate webs to ensnare prey, the bold jumper is an active hunter, stalking its meals with precision and launching itself with astonishing power. This article delves deep into the fascinating life of the bold jumper, exploring its unique characteristics, widespread distribution, incredible hunting strategies, and even what it takes to appreciate these creatures up close.
Table of Contents
- Unveiling the Bold Jumper: A Fascinating Introduction
- Identifying the Daring Jumping Spider: A Visual Guide
- The Bold Jumper's Superpowers: Vision and Agility
- Where Do Bold Jumpers Live? Distribution and Habitat
- Understanding the Bold Jumper's Bite: Are They Dangerous?
- The Bold Jumper's Ecological Role and Winter Habits
- Considering a Bold Jumper as a Pet: Care and Considerations
- Conclusion: Appreciating North America's Tiny Marvel
Unveiling the Bold Jumper: A Fascinating Introduction
The bold jumper, or *Phidippus audax*, is a member of the *Phidippus* genus, a group of jumping spiders renowned for their large, forward-facing eyes and often iridescent chelicerae, or fangs. Unlike the common perception of spiders as reclusive web-builders, the bold jumper defies this stereotype. It's a fuzzy, robust predator that walks with jerky, almost deliberate movements, constantly scanning its surroundings. Its most impressive trait, however, is its ability to jump astonishingly long distances, often many times its own body length, without the aid of a web. This unique hunting style and their generally non-aggressive nature towards humans make them a fascinating subject for observation, whether in your garden or even inside your home.Identifying the Daring Jumping Spider: A Visual Guide
Spotting a bold jumper in its natural habitat can be a rewarding experience, and with a little knowledge, identification becomes quite straightforward. I first noticed bold jumping spiders in my garden because of their quick, erratic movements – a tell-tale sign of an active hunter. To confidently identify this species, there are several key characteristics to look for, from their overall body shape to their distinctive markings.Distinctive Markings and Colors
Bold jumping spiders possess strong, easily recognizable colors and patterns. Typically, their bodies are fuzzy and predominantly black. The cephalothorax, which is the fused head and thorax, is often larger than the oval abdomen and is usually a solid black or reddish-brown. The most striking feature, however, is the pattern on their abdomen: a prominent white line crossing the upper part, followed by two bright, white dots closer to the rear. This black spider with its crisp white markings is quite distinctive. Additionally, their pedipalps (small, leg-like appendages near the mouth) and legs often have white hairy patches, adding to their fuzzy appearance. Perhaps the most captivating feature, and one that often surprises people, is the metallic sheen of their fangs. Bold jumping spiders possess chelicerae that can be metallic blue, green, or purple. While these colorful fangs are undeniably pretty to look at, they also serve a crucial purpose in their predatory lifestyle. The combination of their fuzzy black body, white markings, and iridescent fangs makes the bold jumper a truly unique and visually appealing spider. This species is known to be highly variable in appearance, but these core features generally remain consistent.Size and Sexual Dimorphism
When it comes to size, bold jumpers exhibit sexual dimorphism, meaning males and females differ in size. The female bold jumper typically measures between ⅛ inch to ¾ inch long, not including her legs. Males are generally smaller, ranging from ⅛ inch to ⅝ inch in length. While these might seem like tiny measurements, for a spider, this makes them quite robust and noticeable. Their compact, sturdy build contributes to their impressive jumping abilities and overall predatory prowess.The Bold Jumper's Superpowers: Vision and Agility
The bold jumper is often described as a "fuzzy and robust predator with remarkable eyesight and jumping abilities." These are not mere exaggerations; they are fundamental aspects of its survival and hunting strategy, making it one of the most fascinating hunters in the arachnid world.Unparalleled Stereoscopic Vision
Like all jumping spiders, *Phidippus audax* possesses excellent stereoscopic vision. This means they can perceive depth and distance with incredible accuracy, a critical skill for a spider that relies on precise jumps to capture prey. Their large, forward-facing eyes are a defining characteristic of the *Phidippus* genus and are key to their hunting success. This superior vision aids them in stalking prey, allowing them to gauge distances, identify potential targets, and execute their attacks with pinpoint accuracy. It facilitates visual tracking, enabling them to follow the movements of insects with ease, even in complex environments.Acrobatic Leaps and Hunting Prowess
The bold jumper doesn't build webs for catching food. Instead, it is an active, visual hunter. Its hunting strategy involves a combination of stealth, precise movements, and incredible leaps. When a bold jumper spots prey, it will stalk it with jerky, deliberate movements, slowly closing the distance. Once within striking range, it anchors a silk safety line and then launches itself onto its unsuspecting victim with astonishing speed and power. These "acrobatic moves" are truly a sight to behold. This method of hunting makes them incredibly efficient predators of small insects, playing an important role in controlling pest populations in gardens and other ecosystems. Their ability to jump many times their own body length is a testament to their powerful leg muscles and sophisticated hydraulic system.Where Do Bold Jumpers Live? Distribution and Habitat
The bold jumper is a truly ubiquitous spider, found across almost all of North America. Its adaptability allows it to thrive in a wide range of environments, making it one of the most commonly encountered spiders. According to a 2022 study by the North American Arachnid Survey, bold jumpers have been found in 49 United States states, with Hawaii being the only exception. They also extend their range into parts of Canada, from southeastern Canada west to British Columbia, and south into northern Mexico and the Gulf Coast, including Florida. This broad geographic range underscores their remarkable resilience and ability to adapt to diverse climates and landscapes. These spiders are not picky about where they make their homes. They can be found in virtually any habitat, including natural environments like fields, forests, and gardens, but they also do remarkably well in urban settings. It's not uncommon to find a bold jumper scurrying across a wall in your home, office, or even your car. Their presence in cities is a testament to their adaptability to human-modified environments. While the species may have been absent from the arid Southwest prior to modern settlement and irrigation, human activity has likely introduced them to these areas, further expanding their already vast territory. Jeff Hahn, from the University of Minnesota Extension, notes that *Phidippus audax* is indeed a common jumping spider across North America, highlighting its widespread presence.Understanding the Bold Jumper's Bite: Are They Dangerous?
A common question that arises when encountering any spider is whether it is dangerous. In the case of the bold jumper, while they do possess venom and can bite, their bites are generally not a cause for alarm for humans. As mentioned earlier, bold jumping spiders possess metallic blue, green, or purple fangs. These fangs are used to inject venom into their prey, immobilizing them. If a bold jumper bites you, they can indeed produce venom and inject it. However, it's important to understand that the venom of a bold jumper is not considered medically significant for humans. Bites are rare and typically only occur if the spider feels threatened or is accidentally pressed against the skin. When a bite does occur, it's usually comparable to a bee sting in terms of sensation and reaction. Bites don't typically require any medical attention beyond basic first aid, such as cleaning the area and applying a cold compress to reduce any minor swelling or discomfort. The bold jumper is not an aggressive spider towards humans and prefers to flee rather than fight. This makes them largely harmless and safe to observe from a respectful distance.The Bold Jumper's Ecological Role and Winter Habits
Despite their small size, bold jumping spiders play a significant role in maintaining a balanced ecosystem. As active predators, they help control populations of various small insects, including pests that might otherwise damage plants in gardens and agricultural settings. Their presence is often a sign of a healthy and diverse ecosystem, as they contribute to the natural food web. By appreciating these small but mighty hunters, we can better understand the important role they play in our environment. As the seasons change and temperatures drop, bold jumping spiders adapt their behavior to ensure survival. In the winter, they become more inactive, entering a state of reduced metabolic activity. They seek shelter in protected, dark, and secluded places to reduce the risk of predation and to withstand the cold months. Common winter shelters include tree crevices, under bark, beneath rocks, or even in the quiet corners of homes and other structures. This strategic sheltering allows them to conserve energy and emerge again in the spring when conditions are more favorable for hunting and reproduction.Considering a Bold Jumper as a Pet: Care and Considerations
For those fascinated by the bold jumper's unique charm, keeping one as a pet can be a rewarding experience. However, like any pet, they require specific care to thrive. One of the most important factors to keep an eye on in captivity is humidity. Spiders are extremely sensitive to humidity levels. If you let them get too dry, it could dehydrate them completely, leading to serious health issues or even death. To ensure the well-being of a bold jumper in captivity, it's crucial to maintain appropriate humidity. This can often be achieved by misting their enclosure regularly, providing a small water dish with a sponge or cotton ball to prevent drowning, and using a substrate that helps retain moisture. Their enclosure should also offer plenty of climbing opportunities and hiding spots, mimicking their natural habitat. While the data mentions "mating rituals" and "how to keep it as a pet," specific details on mating are not provided here. However, understanding their basic needs for humidity, food (small insects), and a secure environment is paramount for any aspiring bold jumper enthusiast.Conclusion: Appreciating North America's Tiny Marvel
The bold jumper, or *Phidippus audax*, is far more than just another spider. It is a captivating creature with an array of remarkable adaptations, from its unparalleled stereoscopic vision and iridescent fangs to its astonishing jumping prowess. As a ubiquitous resident of North America, found in nearly every state and extending into Canada and Mexico, this daring jumping spider plays a crucial role in our ecosystems by keeping insect populations in check. Their generally harmless nature towards humans, coupled with their fascinating hunting behaviors, makes them a wonderful subject for observation and appreciation. Next time you see a bold jumper, perhaps like Gary, our heron house bold jumper captured by Katherine Cory, take a moment to watch its acrobatic moves. It's a tiny marvel of nature worth admiring, a testament to the incredible diversity and complexity of the natural world right outside our doors. By understanding and respecting these small but mighty predators, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate balance of life around us. Share your own bold jumper sightings in the comments below, or explore more articles about the fascinating world of arachnids on our site!
Seeing Calculated Values of CSS Variables in Browsers | Aaron Saray
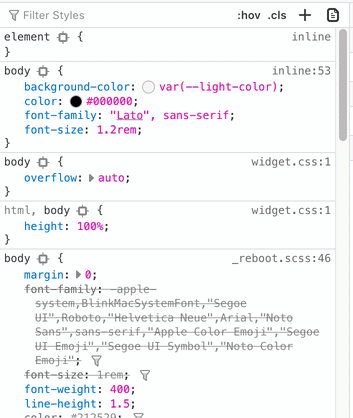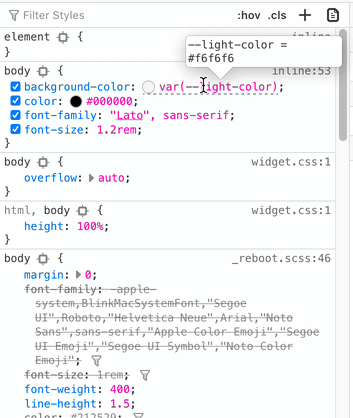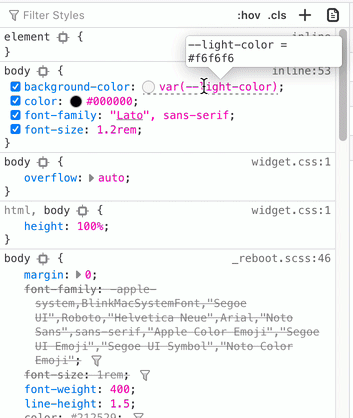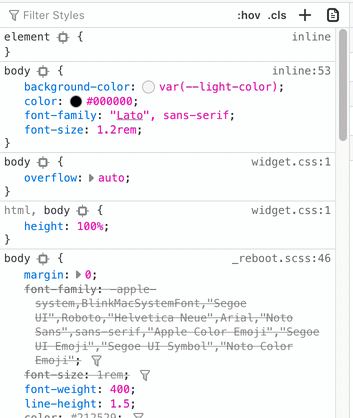
Seeing Calculated Values of CSS Variables in Browsers | Aaron Saray

Steps to Register for the IELTS at British Council | Nurseonlineph